Long term use of cocaine can trigger chronic disease, lowered immunity, or can affect specific organs. In fact, cocaine use impacts all body systems, interrupting normal functions.
More on how smoking, snorting, or injecting cocaine affects the body here. Then, we invite your questions and comments at the end.
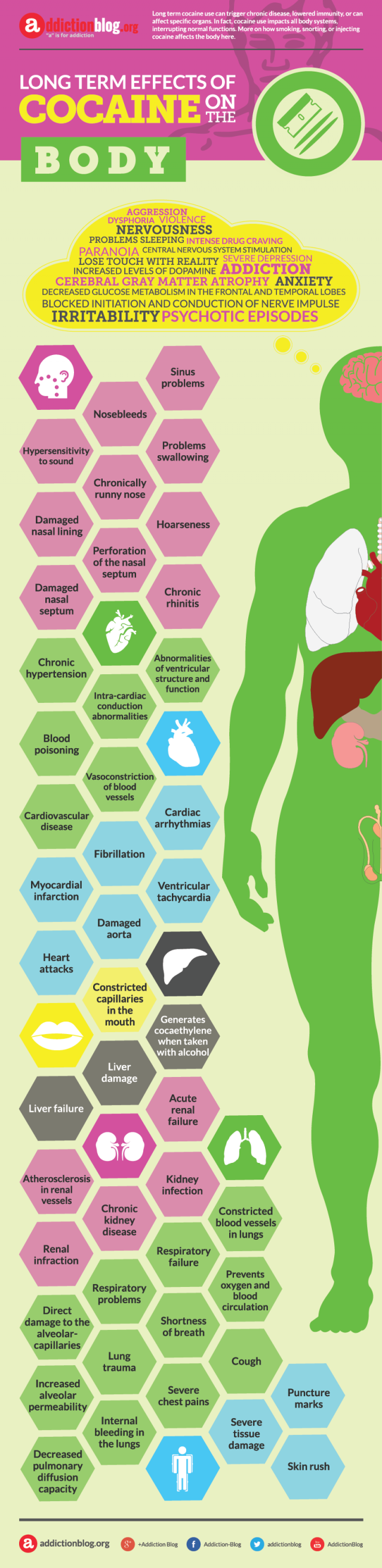
Cocaine effects to mental health
- addiction
- aggression
- anxiety
- cerebral gray matter atrophy
- dysphoria
- intense drug craving
- irritability
- lose touch with reality
- nervousness
- paranoia
- problems sleeping
- psychotic episodes
- severe depression
- violence
Cocaine effects on the ear, nose, and throat
- chronic rhinitis
- chronically runny nose
- damaged nasal lining
- damaged nasal septum
- hoarseness
- hypersensitivity to sound
- nosebleeds
- perforation of the nasal septum
- problems swallowing
- sinus problems
Cocaine effects on the cardiovascular system
- abnormalities of ventricular structure and function
- blood poisoning
- cardiovascular disease
- chronic hypertension
- intra-cardiac conduction abnormalities
- vasoconstriction of blood vessels
Cocaine effects on the heart
- cardiac arrhythmias
- damaged aorta
- fibrillation
- heart attack
- myocardial infarction
- ventricular tachycardia
Cocaine effects on the mouth
- constricted capillaries in the mouth
Cocaine effects on the liver
- generates cocaethylene when taken with alcohol
- liver damage
- liver failure
Cocaine effects on the kidney
- acute renal failure
- atherosclerosis in renal vessels
- chronic kidney disease
- kidney infection
- renal infraction
Cocaine effects on the lungs
- constricted blood vessels in lungs
- cough
- decreased pulmonary diffusion capacity
- direct damage to the alveolar-capillaries
- increased alveolar permeability
- internal bleeding in the lungs
- lung trauma
- prevents oxygen and blood circulation
- respiratory failure
- respiratory problems
- severe chest pains
- shortness of breath
Cocaine effects on the skin
- puncture marks
- severe tissue damage
- skin rash








Related Posts