The Party Drug
Club drugs such as MDMA are super-popular due to the powerful effects they have on the mind and body. People usually take MDMA because it increases their confidence, lowers inhibition, and softens the edges of reality. While ecstasy can make most people feel like they are floating, it can also inflict severe and long lasting damage to the brain and body.
Some reported long-term effects of MDMA include:
- arrhythmias
- depression
- impaired memory and attention processes
- long-lasting confusion
- renal failure
Another important concern of MDMA use is the dangers it has on females while pregnant. Given that most MDMA users are young and in their reproductive years, it is possible that some female users may be pregnant while they experiment with MDMA.
How Does MDMA Get to the Brain?
In this infographic, we visually present how MDMA gets to the brain via the body. We look at basic metabolism and describe the process in a basic 1-2-3 visual description. We welcome you to post your questions regarding MDMA’s effects at the end, in the comments section reserved for questions. We value your questions and try to answer all real-life people as soon as we can.
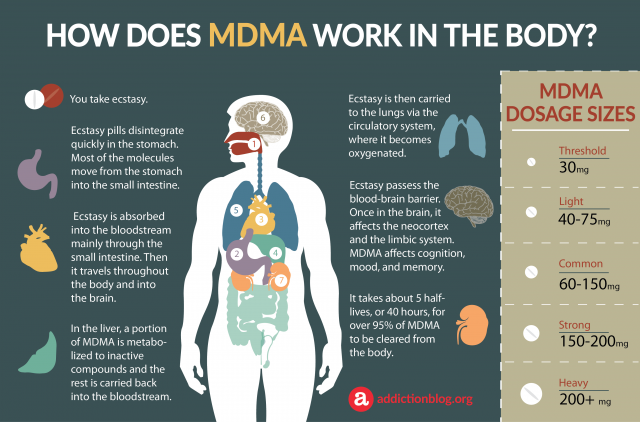
How Does MDMA Work In The Body?
1. You take ecstasy.
2. STOMACH: Ecstasy pills disintegrate quickly in the stomach. Most of the ecstasy molecules move from the stomach into the small intestine.
3. HEART: Ecstasy is absorbed into the bloodstream mainly through the small intestine. Then it travels througout the body and into the brain.
4. LIVER: In the liver, a portion of MDMA is metabolized to inactive compounds and the rest is carried back into the bloodstream.
5. LUNGS: Ecstasy is then carried to the lungs via the circulatroy system, where it becomes oxygenated.
6. BRAIN: Ecstasy passess the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, it affects the neocortex and the limbic system, and affects cognition, mood, and memory.
7. KIDNEYS: It takes about 5 half-lives, or 40 hours, for over 95% of MDMA to be cleared from the body.
MDMA DOSAGE SIZES
- Threshold = 30 mg
- Light = 40 – 75 mg
- Common = 60 – 150 mg
- Strong = 150 – 200 mg
- Heavy = 200 + mg
Any Additional Questions?
If you have any questions that you’d like to learn the answers to, please post them. We will do our best to respond to all legitimate inquiries in a timely and personal manner. In case we don’t know the answer to your questions, we’ll gladly refer you to professionals who can help.
Get Personalized Addiction Treatment Text Support
Receive 24/7 text support right away and at your convenience. There is no obligation to enter treatment and you can opt out at any time.
Want to get help, but not ready to talk? Instead, sign up for text support to receive:
- Resources about addiction and recovery
- Information about our treatment process








Related Posts