What is methadone?
Methadone is a synthetic opioid medication that has been used in the treatment of heroin addicts worldwide since the mid-1960s. However, long-term methadone treatment has been found to cause changes in the brain by affecting nerve cells in the brain. As a result, scientists have observed changes in cognitive functioning, learning ability and memory capacity in individuals who abused the medication.
How methadone affects the brain?
Methadone acts on the same brain structures and processes as addictive opioid drugs do. This helps people who’ve struggled with addiction stop their harmful habits and stay off opioid drugs, however it should never be viewed as a cure for addiction. Methadone should always be used in conjunction with appropriate psycho-social treatments and therapies. The end goal is individuals to eventually be slowly and gradually taken off methadone and continue to live substance free.
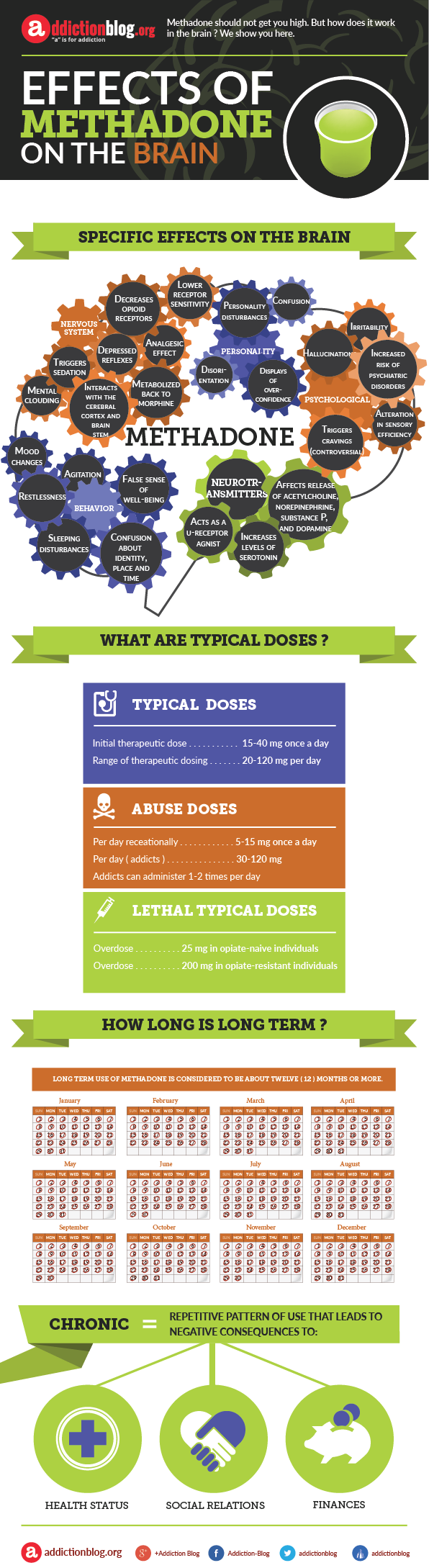
Methadone’s effects on the brain include:
- changes in cognitive functioning
- learning difficulties
- memory problems
- mood and behavior changes
- affected nerve cells and neurotransmitters
- …another one of methadone’s effects is addiction to the medication, although it’s prescribed in the treatment of narcotic addiction and dependence along with treatment of withdrawal symptoms associated with opioid drugs use.
Methadone brain effects questions
Methadone treatment is very useful for opioid drug addicts that have an uncontrolled, compulsive, and harmful behavior associated with narcotics addiction. However, the possible side effects of long-term methadone abuse should not be ignored.
If you have any questions or thoughts about our infographic, feel free to post them in the comments section at the end of the page. Also, if you like our infographic you can SHARE it to continue spreading useful information.








Related Posts