Long term effects of Xanax addiction
Using Xanax to avoid emotional or psychological problems can result in Xanax addiction. Just how addictive is Xanax and can damage caused by Xanax addiction be reversed? We review here.
Use leads to tolerance
Dependence on Xanax is an expected outcome of long-term use of alprazolam for more than 6 weeks, or so. But Xanax use may quickly escalate to unintended and initially unanticipated levels. So how is dependence different than addiction? Mainly, addiction is a psychological condition.
Addiction to Xanax = Self-administering, snorting, taking Xanax other than prescribed and/or increasing Xanax intake without medical advice all lead to Xanax addiction.
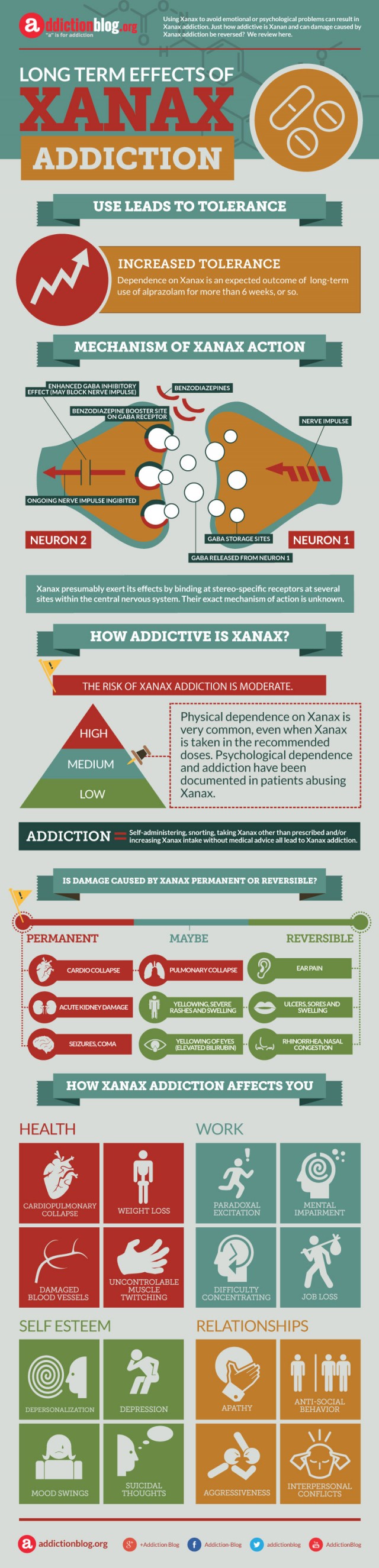
Mechanism of Xanax action
Xanax presumably exert its effects by binding at stereo-specific receptors at several sites within the central nervous system. Their exact mechanism of action is unknown.
How addictive is Xanax?
Physical dependence on Xanax is very common, even when Xanax is taken in the recommended doses. Psychological dependence and addiction have been documented in patients abusing Xanax.
Is damage caused by Xanax permanent or reversible?
Permanent damage that Xanax can cause:
- acute kidney damage
- cardio collapse
- pulmonary collapse
- damage as a result of seizures or coma
Reversible damage:
- ear pain
- rhinorrhea, nasal congestion
- ulcers, sores and swelling
- yellowing of eyes (elevated bilirubin)
- yellowing, severe rashes and swelling
How does Xanax addiction affect you?
Effects of Xanax on health:
- cardiopulmonary collapse
- damaged blood vessels
- uncontrollable muscle twitching
- weight loss
Effects of Xanax on work:
- difficulty concentrating
- job loss
- mental impairment
- paradox excitation
Effects of Xanax on self esteem:
- depersonalization
- depression
- mood swings
- suicidal thoughts
Effects of Xanax on relationships:
- aggressiveness
- anti-social behavior
- apathy
- interpersonal conflicts








Related Posts