Long term effects of cocaine on the brain
In general, cocaine disrupts normal brain function. Brain matter can atrophy. Both judgment and cognition are impaired. And behavior can become aggressive or violent. More adverse effects of cocaine on the brain here.
Specific long term effects on the brain
Long term effects on the nervous system:
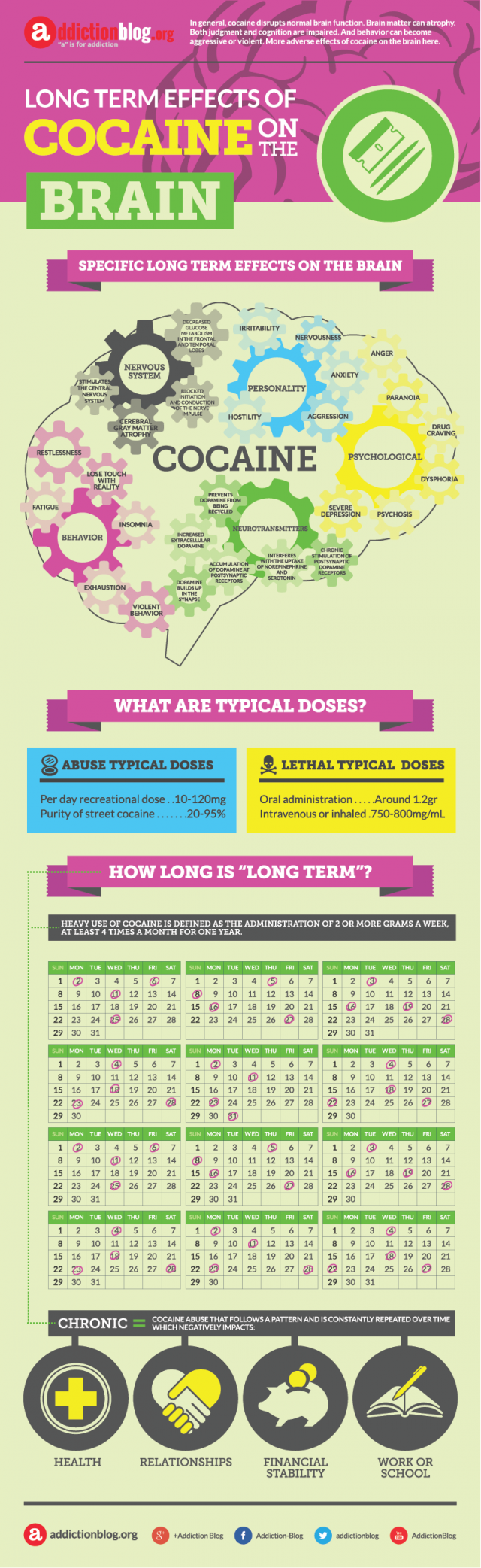
- blocked initiation and conduction of the nerve impulse
- cerebral gray matter atrophy
- decreased glucose metabolism in the frontal and temporal lobes
- stimulates the central nervous system
Long term effects on the neurotransmitters:
- accumulation of dopamine at postsynaptic receptors
- chronic stimulation of postsynaptic dopamine receptors
- dopamine builds up in the synapse
- increased extracellular dopamine
- interferes with the uptake of norepinephrine and serotonin
- prevents dopamine from being recycled
Long term effects on the personality:
- aggression
- anxiety
- hostility
- irritability
- nervousness
Long term effects on the behavior:
- exhaustion
- fatigue
- insomnia
- lose touch with reality
- restlessness
- violent behavior
Long term effects on the psychology:
- anger
- drug craving
- dysphoria
- paranoia
- psychosis
- severe depression
What are the typical doses?
Typical doses of cocaine abuse:
- per day recreational dose …… 10-120 mg
- purity of street cocaine …… 20-95%
Lethal cocaine typical doses:
- oral administration ….. around 1.2 grams
- intravenous or inhaled …… 750-800 mg/ml
How long is “long term”?
Heavy use of cocaine is defined as the administration of 2 or more grams a week, at least 4 times a month for one year. Chronic cocaine use = Cocaine abuse that follows a pattern and is constantly repeated over time which negatively impacts:
- financial stability
- health
- relationships
- work or school








Related Posts