Long term effects of Cocaine addiction
Cocaine is one of the strongest addictive illicit drugs in the U.S., making addiction to cocaine a public health issues. More on the mechanism of action and risks related to cocaine addiction here.
What is addiction?
Addiction = The uncontrollable urge to use cocaine, despite negative consequences to home, work, or social life. Addictive behaviors related to cocaine use often lead to crime. But cocaine addiction is treatable.
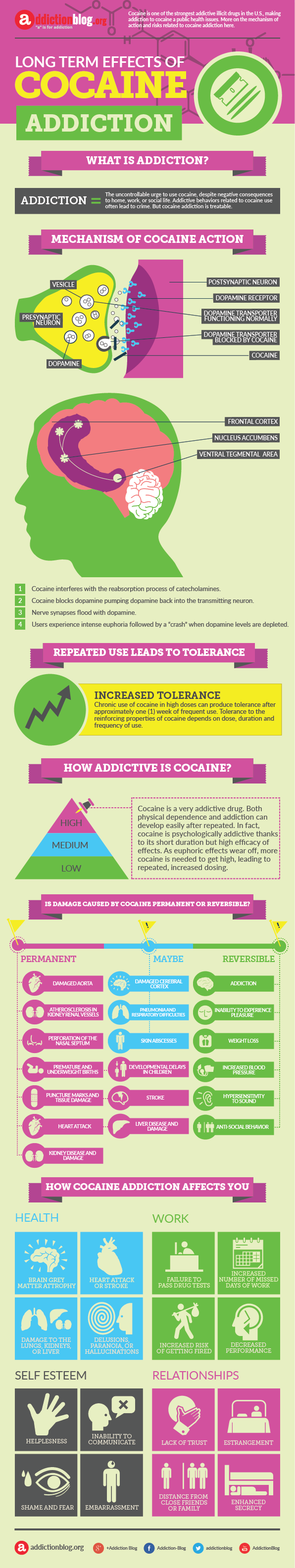
Mechanism of Cocaine action
- Cocaine interferes with the reabsorption process of catecholamine.
- Cocaine blocks dopamine pumping dopamine back into the transmitting neuron.
- Nerve synapses flood with dopamine.
- Users experience intense euphoria followed by a “crash” when dopamine levels are depleted.
Repeated use leads to tolerance
Chronic use of cocaine in high doses can produce tolerance after approximately one (1) week of frequent use. Tolerance to the reinforcing properties of cocaine depends on dose, duration and frequency of use.
How addictive is cocaine?
The addiction potential of cocaine is HIGH!
In fact, cocaine is a very addictive drug. Both physical dependence and addiction can develop easily after repeated. In fact, cocaine is psychologically addictive thanks to its short duration but high efficacy of effects. As euphoric effects wear off, more cocaine is needed to get high, leading to repeated and increased dosing.
Is damage caused by Cocaine permanent or reversible?
Permanent damage that cocaine can cause
- atherosclerosis in kidney renal vessels
- damaged aorta
- developmental delays in children
- heart attack
- kidney damage
- kidney disease
- liver damage
- liver disease
- perforation of the nasal septum
- premature and underweight births
- puncture marks and tissue damage
- stroke
Potentially reversible damage caused by cocaine use
- constricted capillaries in the mouth
- compromised immune system
- shortness of breath and internal bleeding
Reversible damage that cocaine can cause
- addiction
- anti-social behavior
- hypersensitivity to sound
- inability to experience pleasure
- increased blood pressure
- weight loss
How does cocaine addiction affect you?
Health effects of cocaine
- brain grey matter atrophy
- damage to the lungs, kidneys, or liver
- delusions, paranoia, or hallucinations
- heart attack or stroke
Work effects of cocaine
- decreased performance
- failure to pass drug tests
- increased number of missed days of work
- increased risk of getting fired
Self esteem effects of cocaine
- embarrassment
- helplessness
- inability to communicate
- shame and fear
How cocaine can negatively affect relationships
- distance from close friends or family
- enhanced secrecy
- estrangement
- lack of trust








Related Posts