Alcohol and the brain
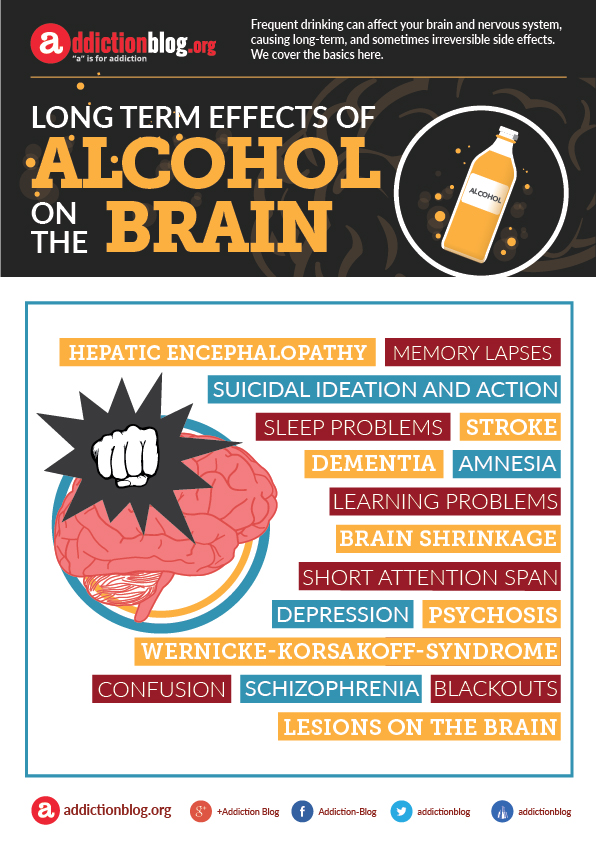
Alcohol affects the parts of the brain that control movement, speech, judgement, memory, thus causing the short term effects of excessive drinking, which include slurred speech, memory lapses, aggressive outbursts and impulsive behavior, and loss of motor coordination. On the long run, drinking large amounts of alcohol for a prolonged period of time can have serious side effects on people’s mind and consciousness.
How alcohol affects the brain?
Alcohol affects the brain’s chemistry by altering the levels of chemical messengers that transmit signals and control our thinking, behavior and emotions. These messengers are called neurotransmitters. Alcohol, in particular, increases the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, while inhibiting the effects of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate at the same time. Alcohol also increases the release of the pleasure chemical – dopamine, at the reward center of the brain.
But, alcohol affects several brain regions in various ways:
- The cerebellum is the center of movement and balance. When we drink, this region in impaired, so staggering and being off-balance can be felt.
- The cerebral cortex is the brain’s region where our thoughts are processed and our consciousness is centered. So, when alcohol is present, it slows down the processing of information from the eyes, ears, mouth, skin, and other senses. It also makes it difficult for people to think clearly.
- The hypothalamus coordinates the automatic functions in the brain and regulates the release of hormones. Alcohol depresses nerve cells in the hypothalamus, thus influencing arousal, ability and performance.
- The medulla is an area of the brain that regulates breathing, consciousness, body temperature, and other automatic functions. When administered, alcohol causes sleepiness by acting on the medulla. It also interferes with the ability to control temperature and respiration, which can be dangerous.
Alcohol affects the parts of the brain that control movement, speech, judgement, memory, thus causing the short term effects of excessive drinking, which include slurred speech, memory lapses, aggressive outbursts and impulsive behavior, and loss of motor coordination. In the long run, drinking large amounts of alcohol for a prolonged period of time can have serious side effects on drinkers’ minds and consciousness.
Get Personalized Addiction Treatment Text Support
Receive 24/7 text support right away and at your convenience. There is no obligation to enter treatment and you can opt out at any time.
Want to get help, but not ready to talk? Instead, sign up for text support to receive:
- Resources about addiction and recovery
- Information about our treatment process
Effect of alcohol on the brain questions
Like our infographic? If you find it to provide useful and shareable information, feel free to share it with others.
Your questions and comments are also welcomed in the section below. We try to provide a personal and prompt answer to all legitimate inquiries.








Related Posts