Heroin Effects On The Mind And Body
Heroin.
The Ultimate High.
Typically, people report feeling like heroes after their first dose. People view heroin as a miracle drug, one that can ease any pain. However, the sense of empowerment is short-lived. And people are left worse than when they started. In fact, most users are usually not aware that the opiate drugs slowly destroys every cell in the body.
Some of the many adverse consequences of heroin use include:
- heart irregularities
- hormonal imbalance
- impaired decision-making abilities
- kidney failure
- neuronal imbalance
- suppressed breathing
In this heroin graphic, we’ll show you how heroin travels through the body from entry to elimination. We’ll describe metabolism and explain how heroin affects each organ of the body. Discover more about how heroin works on the body here. At the end, feel free to send us your questions and feedback. We value the comments of our readers and do our best to answer you as soon as possible.
How Heroin Works in the Brain
Heroin is an opiate drug that physically changes the structure and function of the brain over time. undergoes several chemical reactions in the brain to change into morphine. Then, it binds rapidly to the opioid receptors and causes:
- Anxiety relief
- Euphoria
- Pain relief
- Stress relief
Opiates such as heroin bind to the opioid receptors in the body and mimic natural “feel-good” chemicals (endorphins). Usually, these endorphins are present, albeit at a much lower level. So, heroin boosts the feel-good factor several times more than your normal state. This is what makes it so addictive!
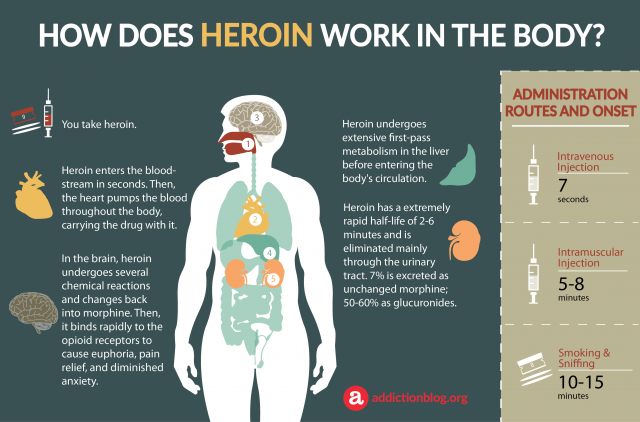
How Does Heroin Work In The Body?
1. You take heroin.
2. HEART: Heroin enters the bloodstream in seconds. Then, the heart pumps the blood throughout the body, carrying the drug with it. It passes through the blood-brain barrier to affect the brain.
3. BRAIN: Once heroin reaches the brain, it undergoes several chemical reactions and changes back into morphine. Then, it binds rapidly to the opioid receptors within the brain to cause euphoria, pain relief, and diminished anxiety.
4. LIVER: Heroin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver before entering the body’s circulation. The liver produces specific enzymes for this purpose.
5. KIDNEYS: Heroin has a extremely rapid half-life of 2-6 minutes and is eliminated mainly through the urinary tract. About 7% is excreted as unchanged morphine and 50-60% as glucuronides. Within 72 hours up to 90% is eliminated in urine.
ADMINISTRATION ROUTES AND ONSET
- Intravenous Injection 7 seconds
- Intramuscular Injection 5 – 8 minutes
- Smoking & Sniffing 10 – 15 minutes
We understand it is difficult to talk to someone about your struggle. Check out our interactive Virtual Consultant to receive your treatment options easily.
Confidential and Free.
Heroin Metabolism Questions
Did we provide you with the basics on the metabolism of heroin?
We hope to have addressed all the answers and information you needed about heroin effects on the brain and body. If you have something to ask us or if the info is not clear, we encourage you to post your question in the comment section below. We’ll try to answer all legitimate inquiries personally and promptly.








Related Posts