Morphine is named after Morpheus, the Greek god of dreams, and it’s one of the most powerful sedative opioids. Here, we review a basic graphic about how morphine affects the brain, and the main problems it can cause. Feel free to LIKE< SHARE<OR COMMENT and we will respond to you personally and promptly!
How does morphine affect the brain?
Morphine causes general central nervous system (CNS) depression, the most common effects being slowed breathing and heart rate. However, morphine also interacts with certain nerve centers and causes chemical reactions in the brain. In the Limbic System, morphine causes increased feelings of contentment, pleasure, and produces short-lasting good emotional feelings. The effects of morphine in the brainstem are a decrease in coughing, which is done by the slowing of breathing and the heart rate.
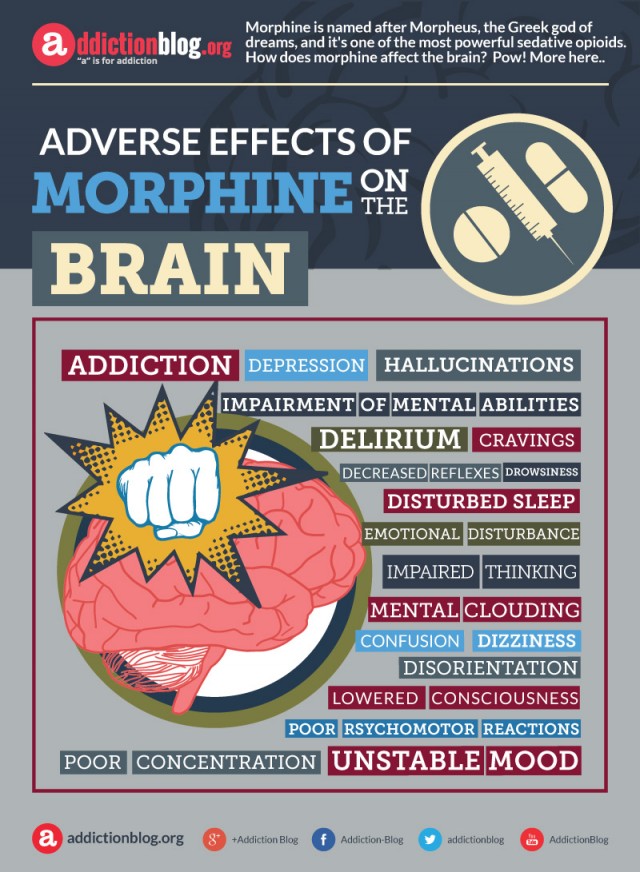
Long Term Effects Of Morphine On The Brain follow:
- addiction
- confusion
- cravings
- decreased reflexes
- delirium
- depression
- disorientation
- disturbed sleep
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- emotional spurs
- hallucinations
- impaired thinking
- impairment of mental abilities
- lower consciousness
- mental clouding
- poor concentration
- poor psychomotor reactions
- unstable mood








Related Posts