Codeine Is Effective…but Risky
Codeine is an opiate painkiller used in the treatment of pain, and sometime to suppress cough. It is usually administered in liquid or pill form and doctors usually prescribe it in combination with acetaminophen.
Codeine has been classified as a Schedule II drug in the Controlled Substances Act, meaning that it has a “high potential for abuse.” When codeine is used under the direction of a clinician, it can be used successfully as a therapeutic aid. But, sometimes people abuse codeine because of the pleasurable and relaxing feelings it produces.
The abuse of codeine in a way other than directed by a medical professional leads to an addiction problem. This includes:
- Taking codeine without a prescription.
- Taking codeine in higher doses or more frequently than prescribed.
- Taking codeine in ways other than prescribed (snorting, injecting, or chewing tablets).
Like many other opiates, withdrawal symptoms from codeine can be severe, keeping you in a cycle of repeated use which you might find difficult to stop.
How Does Codeine Work In The Body?
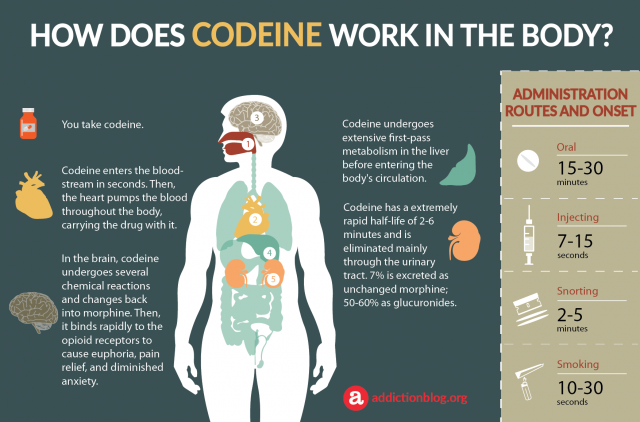
1. YOU TAKE CODEINE: Codeine is usually taken by mouth. It begins working after 30 minutes and its effects last for two hours. Тhe total duration of Codeine effects is 4-6 hours.
2. STOMACH: Codeine might cause some upsets in your stomach upset. For this reason it is highly reccomended for all users to take it in combination with milk or food. The pharmacological properties of codeine are usually the ones that cause stomach pains and an ill feeling.
3. NOSE: Snorting cocaine is considered as one of the methods of abuse. But you may be wondering why do people snort this drug? It is because this method of administration intensifies the drug’s effects, but the long term effects of this are devastating to a person’s health. Snorting codeine on a regular basis exposes people at a high risk of sinus infections. Each Codeine pill contains additive ingredients designed to help it hold its form or shape. The additives contained in the pill can become a source of irritation to the nasal passageways. Any external substance that enters the sinuses repeatedly carries the risk of infection.
4. LUNGS: When Codeine is inhaled it can provoke a histamine response. This means that you’ll feel the same way as experiencing an allergic reaction. Any kind of fluid in the lungs can be fatal. Those who inhaled Codeine and have managed to stay alive were simply lucky. This method of abuse is very dangerous. Codeine is converted into morphine during its first pass through the liver, avoiding the severe histamine response. This is why you should only take codeine orally.
5. BRAIN: Similarly to other opiates, codeine can create a sedating effect. Those who use Codeine usually feel drowsy, especially if they have been using a high dosage or abusing the drug in any way. Due to the slow heart rate users can sometimes faint or feel dizzy. One of the most common symptoms usually felt when taking Codeine are: agitation, confusion, and irritation. If you are taking a higher dose you might experience hallucinations or even convulsions.
6. LIVER: Codeine can cause serious damage to vital organs when used without doctor’s guidance. Self-moderation in doses can cause not just liver intoxication but a life threatening alarm.
7. KIDNEYS: The elimination of codeine is primarily via the kidneys, and about 90% of an oral dose is excreted by the kidneys within 24 hours of your last use.
Codeine Dosage
Codeine is available in multiple formulations including oral tablets of 15, 30 and 60 mg, oral solutions and solutions for injection in varying concentrations. The typical adult, oral dose of codeine for analgesia is 15 – 60 mg every 4 – 6 hours.
Any Questions?
Codeine is a relatively safe and effective medication for relieving pain and cough when used as directed by a doctor. Any abuse of codeine can be dangerous to your health and body. In this infographic, we gave you a visual overlook of the effects Codeine has on each organ of the body. Remember that any kind of abuse can severely damage your health. Stick to the dose your doctor has recommended.
In case you have any further questions, feel free to post them in the section below. We’ll make sure to answer you as soon as we can.








Related Posts